Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines are critical in today’s manufacturing industry. These machines form materials with high-quality precision and speed. But have you ever wondered when CNC machines were invented? Let’s explore records to learn more about the origins and evolution of the CNC machining process.
The Early Beginnings of Machining
The basis of the CNC era is going back a long way, lengthy before the machines we recognize nowadays existed. The first system equipment, designed to update handcrafting strategies and enhance accuracy, was invented in 1751. These early machines paved the way for what might emerge as CNC machining for precision manufacturing. Although these early machines were not PC-pushed, they marked the beginning of automatic machining procedures.
The Birth of Numerical Control (NC)
Fast forward to the 1940s, and we see more excellent superior machines. This changed over time when Numerical Control (NC) machines were added. These machines were the precursors to modern CNC structures. In 1949, John T. Parsons, running on an Air Force research mission, advanced the primary NC idea. He aimed to create a machine to make elements for helicopters, mainly the blades. At the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Parsons, alongside engineers, constructed an experimental milling system that used motorized axes for unique actions.
This gadget was a significant leap forward. It needed to move in exceptional directions and produce elements with more precision than ever before. Although it was a long way from the CNC machines we use today, it set the stage for future advancements.
The Development of CNC Technology
By 1952, further enhancements were made to NC machines. In collaboration with MIT, Richard Kegg delivered the Cincinnati Hydro-Tel machine. This device turned into a vertical milling machine that could be managed routinely. It used punched paper tape to feed commands into the device, which then followed the instructions to shape the material. This improvement represented a primary milestone within the automation of machining tactics.
As the generation advanced, so did the machines. In the 1960s and Seventies, NC machines started transitioning to CNC (Computer Numerical Control). This shift has primarily been caused by the upward thrust of digital technology. CNC milling machines changed analog systems, making the machining method faster and more efficient. By using computers, machinists could enter designs immediately into the gadget, taking into consideration unique control over the gadget’s moves.
How Do CNC Machines Work?
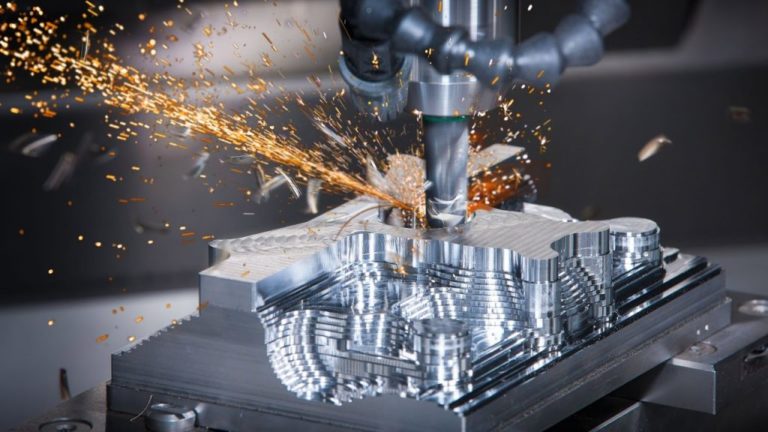
A CNC lathe is a complicated device that uses numerous tools to form substances, including drills, lathes, and milling gear. The critical characteristic of CNC machines is that they perform robotically. The machinist inputs a layout into the laptop, typically inside the shape of a 3-D file, and the machine follows the one’s commands. The device can circulate in more than one instruction, commonly along the X, Y, and Z axes, to reduce and form substances with terrific precision.
More advanced CNC machines can rotate and turn parts automatically, ensuring that the fabric is machined from all aspects without human intervention. This degree of automation permits the manufacturing intricate and complicated parts that would be impossible to create manually.
The Rise of CNC in Modern Manufacturing
As CNC machines became superior, they began to be used in various industries. They were no longer confined to easy slicing and drilling operations. They were now used for mass manufacturing, where precision and speed are essential. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics started depending closely on CNC generation.
One of automated machining’s primary advantages is its ability to work with many exclusive substances. They can handle all of them, whether metallic, plastic, wood, or foam. This versatility has made them a critical device in contemporary manufacturing.
The Impact of CNC Machines Today
Today, CNC machines play a significant role in production. They have revolutionized how products are made, making the system quicker, more specific, and more dependable. What once took hours or days to supply by hand can now be completed in minutes with CNC technology.

The demand for CNC professionals has additionally grown. Skilled machinists who recognize how to function and program CNC machines are in high demand in industries around the sector. As traditional machinists age, their roles change, and CNC professionals are becoming the future of the producing workforce.
Where to discover the best CNC machining gadgets?
Top websites can assist you if you search for the best CNC machining devices. One of the excellent vendors is Junying CNC Machining Center, identified for its superb devices and additives. They provide high-precision manufacturing and various correct and reliable CNC machining tools. They also offer one-of-a-kind custom CNC elements. The website presents focused product descriptions, critiques, and smooth ordering alternatives.
FAQs About CNC Machines
When were CNC machines invented?
CNC machines evolved from Numerical Control (NC) machines, invented in the late Nineteen Forties. The first CNC device was developed in the 1940s while computer systems were being integrated.
What does CNC stand for?
CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control. It refers to a device in which a computer controls the motion of machines, allowing for particular shaping and slicing of materials.
What industries use CNC machines?
CNC programming machines are used in many industries, including aerospace, car, electronics, and scientific tool production. They are vital for quickly producing exquisite, precision elements.
Final Words
CNC machines have come in an extended manner because of their early beginnings. What commenced as a try to automate guide procedures in the 1750s advanced into the very advanced CNC systems we see today. From the improvement of Numerical Control (NC) within the Forties to the PC-driven systems of the present, CNC technology has transformed manufacturing.
CNC machines have revolutionized the production procedure, considering the advent of complicated components with excessive precision. As industries continue to rely on CNC generation, we can expect even more advancements in the future. These machines have changed the manufacturing world, and their impact will continue to grow.