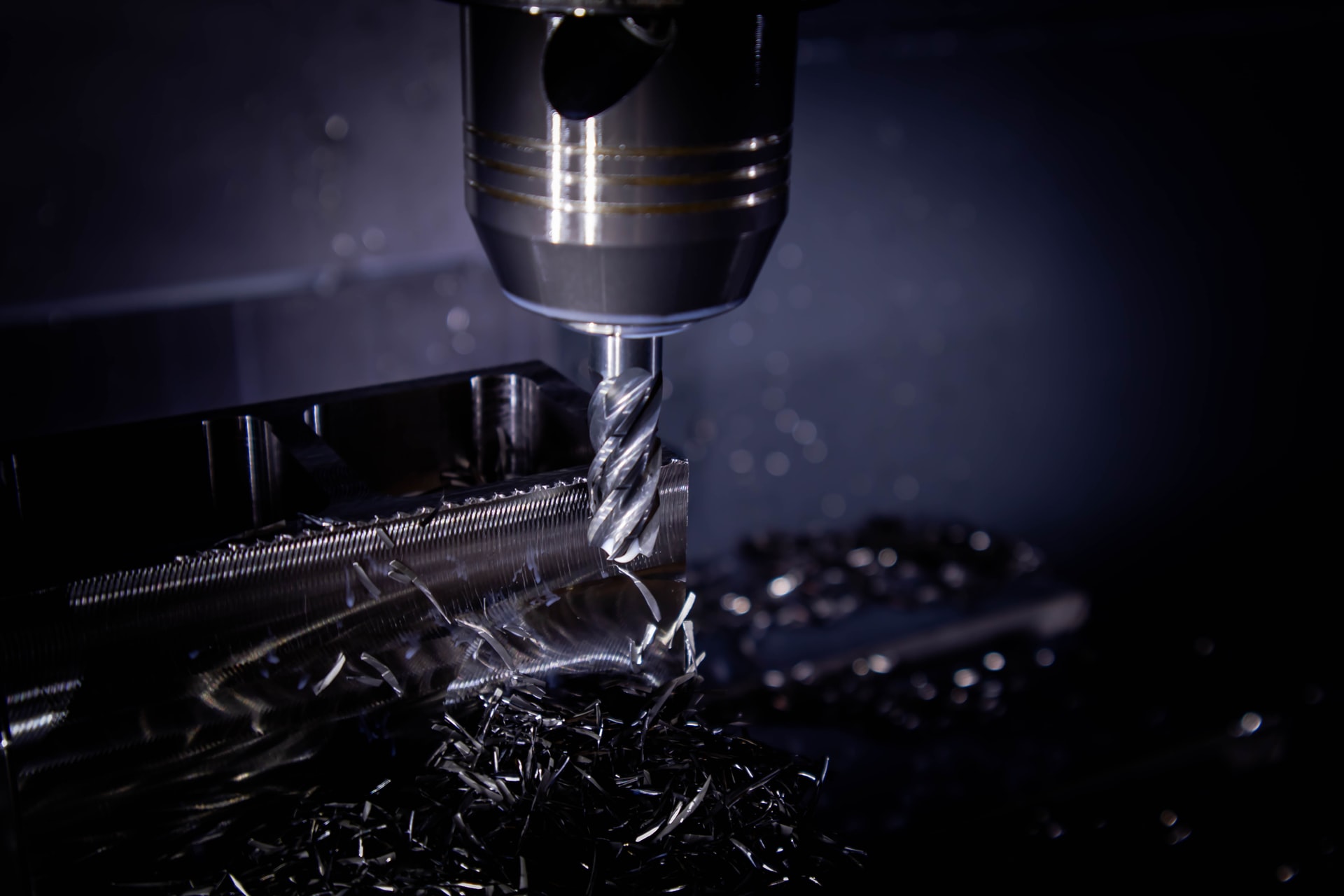
CNC Milling
- Instant Pricing & DFM
- Parts as Fast as 2 days
- Tight Tolerances
- Your IP is safe with us. Learn more.

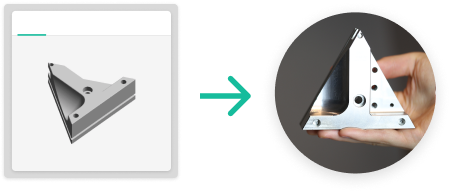
Faster Lead Times
With instant online quotes and rapid production, you can reduce cycle times by as much as 50%.
World-Class Machine Shops
Tap into a highly vetted and managed network of the best machine shops world-wide.

Flexible Pricing
Choose between fast and cost-effective options to find the best price.
CNC Machining Materials
ABS
We can produce parts in just one day thanks to digital manufacturing methods according to our customers’ needs.
ABS
We can produce parts in just one day thanks to digital manufacturing methods according to our customers’ needs.
ABS
We can produce parts in just one day thanks to digital manufacturing methods according to our customers’ needs.
ABS
We can produce parts in just one day thanks to digital manufacturing methods according to our customers’ needs.
ABS
We can produce parts in just one day thanks to digital manufacturing methods according to our customers’ needs.
ABS
We can produce parts in just one day thanks to digital manufacturing methods according to our customers’ needs.
ABS
We can produce parts in just one day thanks to digital manufacturing methods according to our customers’ needs.
ABS
We can produce parts in just one day thanks to digital manufacturing methods according to our customers’ needs.
ABS
We can produce parts in just one day thanks to digital manufacturing methods according to our customers’ needs.
ABS
We can produce parts in just one day thanks to digital manufacturing methods according to our customers’ needs.
ABS
We can produce parts in just one day thanks to digital manufacturing methods according to our customers’ needs.
Finishing Options for CNC Machining
| Name | Applicable Materials | Colors | Can be applied with | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Alodine | Aluminum | Clear, gold | Media Blasting, Tumbling, Type II Anodizing* Type III Anodizing*, Type III Anodizing with PTFE* |
 | Anodizing | Aluminum | Clear, black, grey, red, blue, gold | Media Blasting, Tumbling, Alodine* |
 | Black Oxide | Steel, Stainless Steel | Black | Media Blasting, Tumbling, Passivation |
 | Electroless Nickel Plating | Aluminum, Steel, Stainless Steel | — | Media Blasting, Tumbling |
 | Electropolishing | Steel, Stainless Steel | — | — |
 | Hand Polishing | Acrylic | — | Enhanced cosmetic appearance |
 | Media Blasting | Aluminum, Steel, Stainless Steel, Brass, Bronze, Copper | — | All post processes except Electropolish and Powdercoat |
 | Nickel Plating | Aluminum, Steel, Stainless Steel | — | Media Blasting, Tumbling |
 | Passivation | Steel, Stainless Steel | — | Black Oxide, Electroless Nickel Plating, Zinc Plating, Tumbling, Media Blasting |
 | Powder Coating | Aluminum, Steel, Stainless Steel | Black (20% or 90% gloss), white (20% or 90% gloss) | — |
 | Tumbling | Aluminum, Steel, Stainless Steel, Brass, Bronze, Copper | — | All post processes except Electropolish and Powdercoat |
 | Vapor Polishing | CNC Polycarbonate (Clear, Black) | — | Enhanced cosmetic appearance, near optically clear applications |
 | Zinc Plating | Steel, Stainless Steel | Clear: light blue coating, black: glossy black coating | Media Blasting, Tumbling, Passivation |
* = requires masking
Precision Machining Tolerance
| Metals, PEEK, And ULTEM With Drawing | Other Plastics With Drawing | No Drawing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Dimension | +/- 0.01 mm +/-0.0003 inch | +/- 0.05 mm +/- 0.002 inch | ISO 2768 Medium |
| Hole Diameters (Not Reamed) | +/- 0.008 mm +/- 0.0003 inch | +/- 0.05 mm +/- 0.002 inch | ISO 2768 Medium |
| Shaft Diameters | +/- 0.004 mm +/-0.00016 inch | +/- 0.05 mm +/- 0.002 inch | ISO 2768 Medium |
Depending on the machining process, Fictiv accepts parts up to 48″ in length. If you have larger parts, please chat with our team. Also note that the tolerances listed here are minimums for an ideal case and looser tolerances may be required depending on the process, material choice, or part geometry.
Accelerate Development with Fictiv CNC Manufacturing
- Parts as fast as 2 days
- Tight tolerances
- Instant pricing
- DFM feedback to optimize your designs
- On-demand production updates
- Wide range of materials and finishing options
- Material certifications & certificates of conformity
- Industry leading security standards
- Free dimensional inspection reports
About the CNC Milling Process
With milling, the stock that the part will be cut from is usually a six-sided bar or sheet of material (though it can be also a cylindrical rodi). This stock is fixtured to the bed of the machine and the features of the part are cut using a rotating tool such as a drill or endmill.
Key Aspects of 3-Axis Machining
- The rotating tool can translate relative to the part on X, Y, and Z axes
- The tool is fixed in a vertical or horizontal (depending on the machine) position
- With modern CNC mills, the tool can move in any combination of the 3 axes simultaneously
Key Aspects of 5-Axis Machining
- Capable of the same movements as 3-axes, but with added rotation on X and Y axes
- Typically it is the bed that rotates rather than the toolhead
- The added rotation allows for much more freedon when machining each setup
CNC Milling FAQs
Technical FAQs
General FAQs
The CNC milling process involves a rotating tool that carves away excess material from a stationary workpiece.
CNC turning uses a rotating workpiece, typically used to make cylindrical parts.
A 5-axis CNC milling machine can move a cutting tool in 5 axes, which allows the operator to simultaneously hit five different sides (or more) of a part depending on the design complexities. Resultantly, the tool is highly capable of creating highly complex products and parts.
With a 5-axis machine, the X, Y, and Z-axes are similar to a 3-axis machine layout. The table then rotates along the A-axis, as it does with the 4-axis. However, the 5-axis machine involves the pivoting action at the joint of the table, followed by rotation along the C-axis, which defines the fifth movement.
A CNC router moves the spindle around a stationary table and is primarily designed to operate at high speeds.
A CNC mill typically moves the workpiece along a linear axis, making cuts through the driving force of rotational speed.
The most commonly used materials in CNC milling are metals, such as aluminum, brass or steel and plastics such as ABS, acrylic, polycarbonate, and polypropylene.






