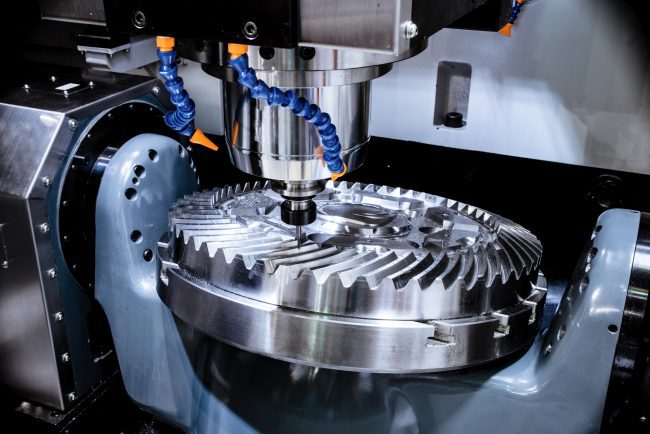
What Is an Axis in CNC Machines?
In CNC machining, an axis acts like a guide, steering the cutting tool. It decides how the tool moves in various directions, which is vital for accurate material shaping. CNC machines usually feature three main axes: X, Y, and Z. Here’s what each axis does:
X-axis: Controls horizontal movement.
Y-axis: Manages vertical movement.
Z-axis: Governs depth.
By understanding axis functions, you can master CNC technology, ensuring precise manufacturing and high-quality output.
Why Axis in CNC Machines Matter?
For CNC machines, axis knowledge is essential to quality machining. To precisely manipulate tools, CNC, or computer numerical control, uses axes. X, Y, and Z are the three axes that move in distinct ways. Things are more accurate and efficient when one is aware of how they interact.
The Z-axis determines how deep the tool can go, the Y-axis moves up and down, and the X-axis moves side to side. By understanding these movements, operators can make complex designs easily. This understanding helps reduce mistakes and waste.
Also, knowing about axes makes programming easier. Operators put in coordinates for each axis. This guides the machine to make the shapes we want. Being good at using the axes makes programming smoother.
Types of Axis in CNC Machines
Here are the main types of axes in CNC machines:
X-axis: The X-axis moves the tool side to side along the workpiece. It controls side-to-side movement. This lets the tool cut across the material.
Y-axis: The Y-axis moves the tool up and down along the workpiece. It controls up-and-down movement. This lets the tool cut along the material.
Z-axis: The Z-axis controls how deep the tool goes into the workpiece. It decides how deep the tool cuts into the material. This allows for precise shaping and engraving.
A-axis: Some CNC machines have an A-axis. This rotates the workpiece around a side-to-side axis. This axis is good for making round or symmetrical shapes.
B-axis: The B-axis rotates the tool itself around an up-and-down axis. It lets the tool come at the workpiece from different angles. This expands the range of possible cuts and shapes.
C-axis: The C-axis, like the B-axis, rotates the tool around a side-to-side axis. It gives more flexibility for machining complex shapes and surfaces.
How Axis Setup Works in CNC Machines?
CNC machines are amazing tools for making things. They have changed how we make precise parts. A big part of how they work is the setup of the axis. This setup controls how the machine moves and places the cutting tool. Let’s look at the basics of axis setup in CNC machines.
Firstly, what do CNC machines’ axes mean? The cutting tool’s motion is set by its axes. Three primary axes are found on most CNC machines: X, Y, and Z. The Z-axis determines how deep the tool can go, the Y-axis moves up and down, and the X-axis moves side to side.
Let’s now examine various axis configurations. Numerous configurations exist, including 4-, 5-, and even 3-axis arrangements. How exact we want to be and how complicated the parts are will determine which option is best.
The cutting tool in a 3-axis configuration can move in three directions: X, Y, and Z. Simple pieces with straight cuts work well with this arrangement, which is frequently utilized for simple tasks.
Adding another rotating axis, a 4-axis arrangement moves higher. This enables the cutting tool to spin along a fourth axis in addition to the X, Y, and Z movements, enabling more intricate cuts and forms.
At last, a 5-axis configuration raises the bar for precision. This configuration allows The cutting tool to travel along the X, Y, Z, and two additional rotational axes. This reduces the need for repeated setups and increases efficiency by enabling the creation of extremely complicated parts with complex shapes.
Moving on to why axis setup is important, it directly affects what CNC machines can do. A machine with more axes can do a wider range of tasks and make more complex parts with higher precision.
Also, understanding axis setup is key to making manufacturing processes better. By choosing the right setup for each job, makers can cut down on time and costs while making quality and efficiency better.
How CNC Machines Work?
CNC machines are key in modern making. They move and work in a very exact way. To use them well, you need to know how the axes work.
Controlling Movement
CNC machines move in different ways. The X-axis moves from side to side. The Y-axis moves up and down. The Z-axis moves forward and backwards.
These axes work together to do complex jobs with great accuracy. They control the cutting tool to make detailed shapes.
Being Precise and Accurate
The axes help CNC machines be precise and accurate. Each axis helps keep the size right and meet tight limits in the parts made.
With more advanced setups, like 5-axis CNC machines, makers can be even more precise. This lets them make complex parts with detailed features that meet very high standards.
Working Together and In Sync
The axes need to work together and in sync for smooth jobs. CNC machines use smart control systems to make sure the movement is smooth and the axes work together well.
By keeping the axes in sync, CNC machines can follow complex paths and shape parts efficiently. This makes the part quality consistent and cuts down on the need for people to step in, which boosts productivity.
Using Axes in CNC Machining
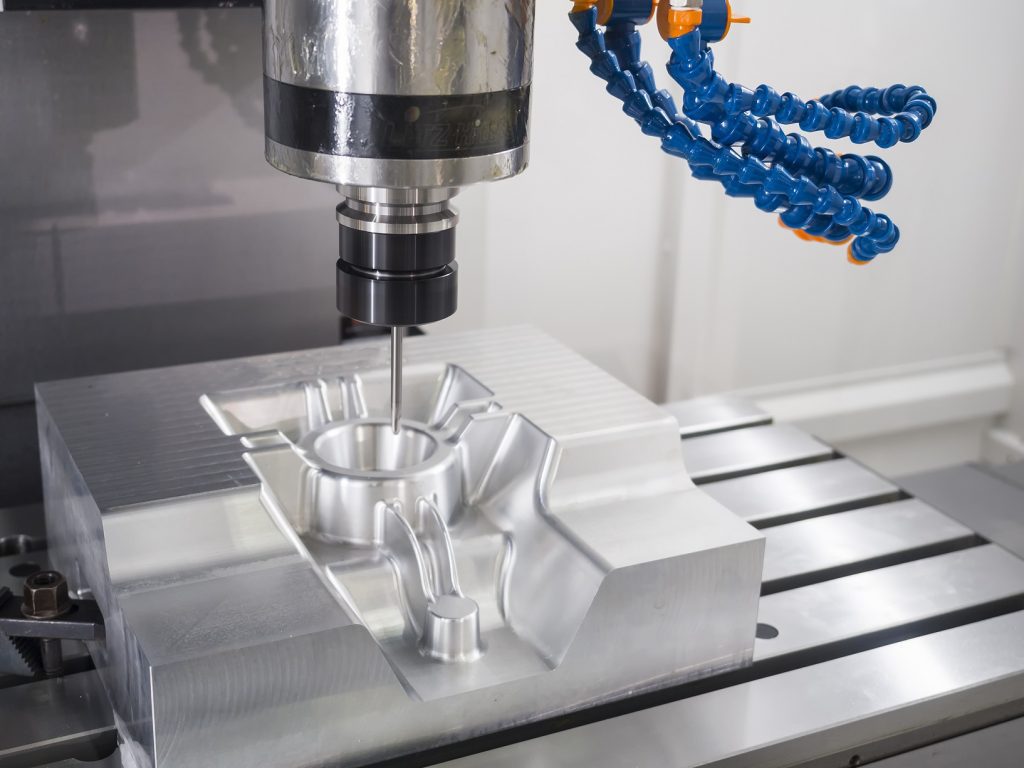

Making Processes
Axes in CNC machines are key in many making processes across industries. From milling and turning to grinding and laser cutting, CNC machines use axes to do a wide range of jobs.
Being able to control movement along many axes lets makers create parts with complex shapes and detailed features. This flexibility makes CNC machining good for both making prototypes and mass production.
Uses in Industries
CNC machines are used in many industries, like car making, aerospace, medical, and electronics. In car making, CNC machining is used to make engine parts, transmission parts, and body panels very precisely.
Aerospace makers use CNC machines to make important parts like aircraft structures, turbine blades, and aerospace alloys. The precision and repeatability that the axes control gives are key to meeting strict aerospace standards.
Examples of Using Axes
Examples of using axes in CNC machining include 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis setups. In a 3-axis setup, the cutting tool can move along X, Y, and Z axes, which is good for basic milling and drilling jobs.
With a 4-axis setup, makers can make the cutting tool move circularly. This lets them shape round and curved surfaces. This makes CNC machines more flexible for making complex parts.
Lastly, a 5-axis CNC machine adds two more rotating axes. This lets it machine from many angles at the same time. This lets it make very detailed parts with fewer setups, which cuts down on time and costs.